openSUSE:Hoofdkenmerken
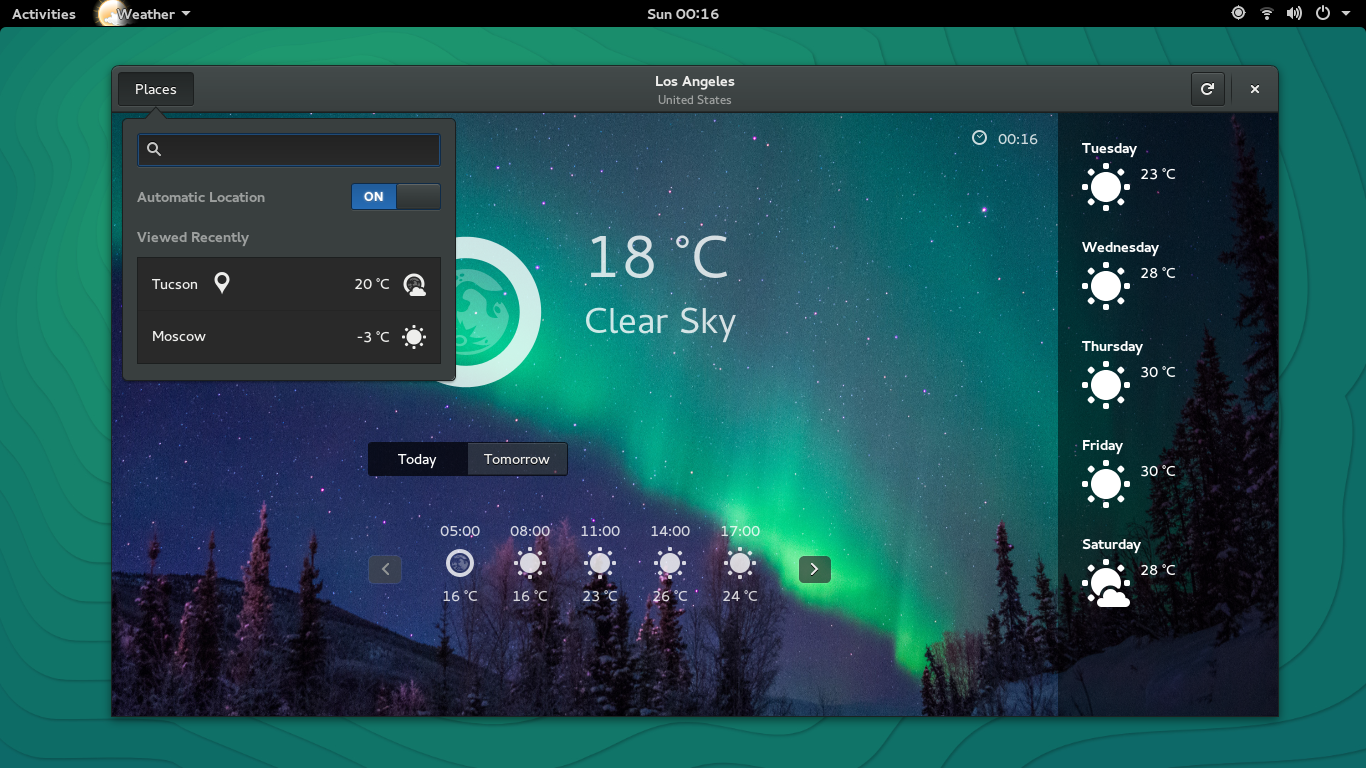
Schermafdrukken gaan hier heen
Inhoud
- 1 Systeem (onder water)
- 2 Free Desktops
- 3 New and updated applications
- 4 Scientific
- 5 Financial
- 6 Web Stack
- 7 Development tools, IDEs, toolchain
- 8 Security
- 9 Games
Systeem (onder water)
Deze pagina is klaar voor 13.2 - op zoek naar 13.1 om ze toe te voegen? U bent laat, maar hulp is toch welkom - ga hier heen. Schermafdrukken gaan hier heen.
| Dit artikel is nog maar gedeeltelijk vertaald. Als u mee wilt helpen met vertalen lees dan Wiki vertalen naar het Nederlands. |
- mkinitrd was replaced by dracut
Linux kernel 3.16
The system operates with the 3.16 kernel patch. Linux 3.16 comes with improvements for Nouveau the open source driver for NVIDIA cards as well as more features for Intel and AMD graphics. This new kernel improves the performance of Btrfs, as the default file system for the root partition, and XFS.
Performance
Changes In Filesystems
- btrfs is the new default filesystem
- The btrfs filesystem snapshot tool ‘Snapper’ leaps from 0.1.7 to version 0.2.4, which adds the ability to boot right into a snapshot to recover from corruption of important files on the system (like bash).
Networking
- the old ifup mechanism was replaced by Wicked
Persistent Live Media
Live images are now persistent by default, so you can write the Live image to a USB stick, boot from it, store your data and install your favourite apps in it and carry it around as your own portable configured operating system. Inside the hood, they use BTRFS as the persistent filesystem, so the Live system is fast and stable from the get go.
openSUSE technologies
YaST: revamped installer
The new openSUSE 13.2 installer comes with several changes targeted to make the installation process easier and more welcoming to new users. Those changes include:
- New installation work flow. Up to 13.1 the installation was followed, after the first reboot, by the so called “2nd stage” phase, in which several additional settings needed to be configured. The new process is more straightforward removing the second stage. As soon as the basic installation is over, the system is ready to use.
- You can even skip the last step and, instead of actually installing the system, export the configuration as a complete AutoYaST profile. In addition, by default AutoYaST configuration is also exported at the end of every installation and available in the new system.
- Better and smarter automatic proposals.
- Less cluttered configuration options: some advanced configuration options (like LDAP user authentication, printer configuration,...) have been removed from the installer. These options are still available later after the system is installed and also through AutoYaST.
- Brand new look and feel focused on usability.
YaST: drop support for Grub Legacy
As a first step to improve the robustness of one of the most challenging and relevant aspects of Linux installation and configuration, YaST will drop support for Grub Legacy in openSUSE 13.2 focusing on GRUB2, which was already the default and recommended option in openSUSE 13.1. Of course, Grub Legacy can still be manually installed but removing it from YaST will enable the developers to work on a more advanced approach to managing the bootloader in future openSUSE releases.
YaST: other improvements
Several parts of YaST have been improved and cleaned up after the automatic conversion from YCP language to Ruby shipped with 13.1. Compared to that version, the new YaST is:
- Faster
- More stable
- Better integrated with systemd, btrfs and the other cutting edge technologies included in openSUSE 13.2.
YaST: more accessible to developers
Together with the abovementioned cleanup, the YaST team have put effort into adding developer's documentation and unit tests to YaST, with the goal to lower the barrier entry for technical contributors. In addition, to integrate all the new and not so new documentation, a new landing page targeted to developers have been setup in http://yast.github.io/ [not finished yet, but we'll try to have it ready for release date].
Other features and changes
- PulseAudio was upgraded to version 5, which adds BlueZ 5 support (A2DP only), Reimplementation of the tunnel modules, Native log target support for systemd-journal, and many bug fixes. You can read more about it here
Free Desktops
KDE
- Kde desktop 13.2.png
KDE 4.14
- Kde kontact 13.2.png
Kontact
- Kde widgets 13.2.png
Widgets
- Kde yast 02 13.2.png
YaST
KDE 4.14, dedicated to Volker Lanz, a long time KDE member who passed away last April, provides users a familiar look, feel and functionality; KDE is a good option for users transitioning from another OS.
The Desktop
OpenSUSE 13.2 ships with the latest latest stable version of the long-term support Plasma Workspace (4.11.12). Long-term support means no new features, but improved stability and bug fixes.
Applications part of the Software Compilation have been updated to their latest stable releases (4.14.2; announcement) as well.
The Applications
- Calligra
The latest stable release of the Calligra office suite (2.8.5) is available, bringing new features and improvements across all the board.
- KDE Telepathy
openSUSE 13.2 ships the KDE Telepathy stack, an alternative set of applications to handle instant messaging, provided as an alternative to the venerable Kopete. Among the features offered by the version shipped in the distribution there are off-the-record (OTR) encryption for instant messaging, multi-protocol support (including popular IM services) and a set of applets for the Plasma Workspace to handle online status and messaging.
- KDevelop 4.7
For the users who are also developers, the distribution offers the latest version of the fully featured IDE KDevelop, the last of the versions based on the 4.x KDE development platform. In addition to C++, there are plugins available which extend its support for additional languages such as PHP or Python.
- KDE Frameworks 5 and Plasma 5
KDE Frameworks 5, a series of development libraries on top of Qt 5 made by KDE, is present in its latest stable release (5.3.0). The libraries co-exist with the existing 4.x variants, allowing development of KF5-based applications within a stable 4.x based workspace.
As a technical preview, Plasma 5.1, the next generation workspace by KDE, is also present as an option for the brave users and tester willing to try it and report bugs to the developers.
- Under the hood
KDE applications requiring multimedia are now based on the 1.0 version of the GStreamer multimedia framework, allowing a noticeable reduction in dependencies.
The Qt5 toolkit has also been updated to the latest version (5.3.2).
GNOME
openSUSE 13.2 comes with a much improved GNOME experience with GNOME 3.14.1 (openSUSE 13.1 had GNOME 3.10).
- OS1320 GNOME-User-Menu.png
GNOME 3.14 desktop
- OS1320 SPG Applications Overview.png
Activities overview
- OS1320 SPG Totem-Tears-Of-Steel.png
Video player
- OS1320 GNOME Software Featured.png
Software App
Interface improvements
- Animations in the Shell and applications
The Shell feels more interactive now that it has gained pretty-but-subtle animations, for example, when switching to the applications overview and maximizing and restoring windows. Applications have also picked up support for animated transitions, and these are already implemented in core applications including clocks, weather, maps among others.
- Perfect HiDPI screens support
GNOME 3.14 comes with perfect HiDPI support so that the desktop and all core GNOME applications look pretty on high-definition screens.
- Support for captive portals when connecting to wifi
When connecting to a WiFi connection that requires you to log-in through a web-page, e.g., at airports, GNOME now automatically launches the log-in page in a browser as soon as the connection is established.
- Configurable Network Sharing
GNOME now remembers which networks you want to enable sharing your personal files, media and screen on and therefore is completely privacy respecting. Additionally, sharing can be controlled and configured from Settings.
- Much improved searching in GNOME-Shell
Many more GNOME-Shell search providers (clocks, software, calculator...) make searching from the shell much more user-friendly and effective. You can, in addition to searching for files and documents, also search for Notes, open terminals, current time around the world by city names and so on. Typing in arithmetic operations in the search-bar gives you the result for the calculation straight on the shell overview.
- Improved Geolocation support
Geolocation support in GNOME has been vastly improved, with many applications making use of this improved support. Thus, clocks, weather, maps and Date and Time Settings all benefit from being geolocation enabled, showing appropriate information based on you current location. E.g., weather defaults to showing the weather at your current place when launched after geolocation is enabled in Settings. For the privacy concerned, Settings provides a way to toggle geolocation support on/off across all applications.
- App-folders in GNOME Shell Application Overview
To reduce cluttering in the Application Overview, GNOME Shell now comes with Sundry and Utilties applications packed in respective app-folders, showing these applications only when the app-folder is clicked on. In an openSUSE touch, the YaST modules come in their own app-folder now. This makes it easy to access any YaST module straight from the Shell without the added overhead of cluttering the overview.
- Touch-screen gestures now supported
GNOME shell has gained full support for touch-screens, even enabling several utility multi-touch gestures for convenient switching to application overview, switching workspaces, and others. Indeed, this has allowed, for the first time, the notifications bar to be accessible by touch, mapping it to the swipe-up gesture.
GNOME Applications
- GNOME Maps gained support for route planning
Available as a preview application in openSUSE 13.1, Maps has stabilized and now comes with a host of advanced features. Prime among them is the support for route planning which is implemented using the open-source GraphHopper library.
- GNOME Software, the new way of application management
Because the regular user is not interested in 'packages', which are a technicality, but rather in Applications, Software provides the Appstore featuring just applications. Using AppStream metadata, as published in the repository metadata, Software brings a much desired convenience to application management on GNOME, making it easy to find, install and update applications.
- Google Account support for GNOME Photos
In addition to photos on your local computer, Photos can now also access photos on your Google/Picasa account. In addition, sharing to home media servers is also supported via DLNA.
- Playlist support in GNOME Music
Music gained the long awaited playlist support and is able to play music from remote systems (using the search capability). It is now the default music application on openSUSE 13.2 GNOME, and comes with a rich list of interface improvements since the version in the previous release.
- All new Videos interface
Videos (Totem) was completely redesigned in the 3.12 cycle, making it more of a match to the GNOME3 application design guidelines and also picking up the ability to stream online videos from several pre-configured channels. The navigation toolbar now is overlaid on the actual video playback area and hides automatically when not in use, thus making the application interface uncluttered and allocating maximum screen space for the playing video. Beyond the (great!) new look, it still uses the trusty gstreamer library for smooth beautiful playback.
- Modern interface for Document-viewer
Evince, the document viewer, comes in a vastly redesigned interface with a header bar that reduces vertical space usage, ensuring that it is your document that takes up maximum screen real-estate and not the application bezel. It also comes with support for pinch-to zoom gesture support on the touch-screen.
- Polari -- A modern IRC client
Polari, a sleek, modern IRC client, replaces XChat as the default IRC application. For XChat aficionados, it is still available for install from the default repositories.
- Other improvements
Several applications have ratcheted up significant improvements since the last release.
- Boxes has gained support for snapshots
- Documents now provides a way to delete selected documents
- Meld, the file/directory diff-viewer gets gtk-3 interface
- GEdit has a brand new interface with a pop-over based file open dialog
- Bluetooth setting has been redesigned to make it easier to configure
- Lots of visual refinement has gone into the desktop and applications to provide a more consistent, stylistic view across the board
GNOME Infrastructure / internals
- Improved support for MultiTouch input devices, including gesture support
- Wayland support greatly inproved, including Drag'n'Drop, Touch, and GNOME Classic Mode
- Geolocation: In addition to wifi-geolocation, GNOME now use Mozilla Location Service for 3G-geolocation and geoip. This means increased accuracy, especially in the long term.
Xfce
openSUSE 13.2 will ship with the same Xfce version as its predecessor, as XFCE 4.12 isn’t out yet. But worry not, the Xfce team has been working diligently so there have been under the hood changes to allow better integration with systemd and upower >= 0.99. Also, to mention a couple of most user-visible changes, there are new version so of gigolo, the midori web browser (with a much improved adblock functionality and spell checking) and a fully redesigned Parole. xfburn 0.5.2 now supports Blu-Ray and large files through ISO9660 level 3. More noticeable will be the changes to the core XFCE4 plugins:
- xfce4-clipman-plugin 1.2.6 brings a new QR-code generator and the ability to skip actions via a keyboard shortcut
- xfce4-timer-plugin 1.6.0 has the ability to rerun a timer from the alarm notification
- Whisker Menu 1.4.0 introduces a new command to launch menu editor and to switch users, support for custom menu files, drag and drop for launchers to panel or desktop, added search actions, the ability to browse commands and to hide them, as well as hiding category and launcher icons.
- xfce4-power-manager 1.4.0 brings a completely revamped and vastly simplified UI with a new panel plugin to show the status of batteries, switch to presentation mode
- xfce4-taskmanager 1.0.1 features UI fixes and bugfixes
- xfce4-terminal 0.6.3 has improved URL matching, a new light solarized color scheme and the usual bugfixes
openSUSE 13.2 will also introduce a new custom theme for the notification daemon (xfce4-notifyd).
LXDE
Who said that LXDE was dead? It has recently reached version 0.99.0 and is now on the way to version 1.0. However, openSUSE 13.2 ships LXDE 0.5.5, with its packages updated to the latest available at package freeze time.
- 13.2 - LXDE - LXAppearance.jpg
Appearance manager
- 13.2 - LXDE - Weather Plugin.jpg
LXPanel Weather plugin
Aplications
Each and every LXDE core application and component has been updated. An exhaustive bug fixing has been performed to increase the overall system stability and performance. In addition, applications gained new features and improvements:
- PCManFM 1.2.2, the file manager, has now dual-pane support; the ability to control the status bar visibility and to hide elements in the toolbar, or the toolbar itself; new options to open automounted media in a new tab or folders from desktop in a new window, and to copy path(s). The path bar can use buttons instead of a location text field allowing breadcrumb navigation of the filesystem. As an extra bonus, basic menu editing functions are present if you select Applications in the Places panel.
- LibFM 1.2.2 is one of the LXDE core libraries and PCManFM releases are closely tied to it. It has gained many features that are reflected in other components. It has also received enhancements and an extensive bug fixing, so all of its clients are now more stable than ever.
- menu-cache 0.7.0, another core component used to generate a cache version of the applications menu, has been improved to be faster and more complete than it has ever been before.
- LXPanel 0.7.1 can now close all windows within a group, and it has gained basic multi-monitor support, a new keyboard layout toggle dialog and supports adding accelerators to the main menu. There are also the new plug-ins 'launchtaskbar' (which combines functionality from 'launchbar' and 'taskbar') and 'weather'. Dragging of task buttons in the launchtaskbar has been improved and it now allows the dragging of applications in the menu so they can be dropped elsewhere (the only supported case seems to be drop them onto PCManFM/desktop at the moment). Last but not least, you can customize the panel to your liking thanks to the new support for custom
gtkrcfiles, a.k.a. theming support. - LXRandR 0.3.0 GUI frontend for
xranrdhas gained new monitor positioning options, a confirmation dialog on mode(s) change, and improved automatic monitors detection. - LXCC, LXDE Control Center, includes now the previously missing translations.
- and much more...
Interface improvements
The desktop has moved from Clearlooks GTK theme to Adwaita. This gives to the desktop a more uniform appearance when using both GNOME and LXDE applications at the same time. The theming issues present in 13.1 are now solved and you won't have any problems to select icon, GTK or mouse cursor themes. If you want a better integration of Qt applications, just run qtconfig and select GTK+ from the GUI Style drop down list.
Openbox presents a new theme that matches with Adwaita too.
Finally, the panel has dropped that old black background image and it now uses a color that fits better with the overall appearance of the desktop. Not a big revolution but hopefully a step forward.
Third party applications
Third party applications that complete the desktop have also been updated: Galculator 2.1.3, Parcellite 1.1.8, Viewnior 1.4, Xarchiver 0.5.4 (that now supports test/verify archives in addition to xz/tar.xz and RAR 5 file formats), ...
There has been some changes in the default pattern intended to produce a better desktop experience:
- Leafpad is now the default text editor for basic editions and Beaver has been dropped (but is still available if you want it) in favor of Geany for advanced task,
- inclusion of gcolor2 color picker so you don't have to open a graphics program just to select a color,
- xfce4-screenshooter replaces mtPaint for screen capture tasks, allowing more options and leaving mtPaint for digital photos manipulation.
Want more?
Even though it is not an officially supported repository, X11:lxde provide the latest available versions of the desktop components and bug fixes for them. Visit the LXDE repositories wiki page to learn how to add this repository to your system.
Want even more? If you're a brave user, LXQt, the fusion of LXDE and Razor-qt projects and future replacement for LXDE written using Qt, is available in our repositories. Keep in mind that LXQt is in an early stage of development (version 0.8 has just been published) and still lacks features and maturity compared with LXDE. Again, this is not an officially supported repository.
In short, this could be one of the best openSUSE LXDE releases of all the times. Try it!
MATE
After GNOME 2.x passed the torch to GNOME 3, GNOME 2.x environment was forked and now it’s called MATE Desktop Environment. The MATE desktop is now officially available under openSUSE 13.2 with MATE version 1.8.1, the latest stable release. It provides an intuitive and attractive desktop environment using traditional metaphors for Linux and other Unix-like operating systems.
Applications
- Mozo (1.8.0) is MATE Desktop menu editor, using the freedesktop.org menu specification.
- Caja (1.8.2) is the official file manager for the MATE desktop. It allows to browse directories, preview files and launch applications associated with them. It works on local and remote filesystems.
- Marco (1.8.2) is a small window manager, using GTK+ to do everything. It is developed mainly for the MATE Desktop.
- Pluma (1.8.1) is a small, but powerful text editor. It has most standard text editor functions and fully supports international text in Unicode. Advanced features include syntax highlighting and automatic indentation of source code, printing and editing of multiple documents in one window. plumais extensible through a plugin system, which currently includes support for spell checking, comparing files, viewing CVS ChangeLogs, and adjusting indentation levels.
- Eye of MATE (1.8.1) is a simple graphics viewer for the MATE Desktop which uses the gdk-pixbuf library. It can deal with large images, and zoom and scroll with constant memory usage. Its goals are simplicity and standards compliance.
- Atril (1.8.1) is a document viewer capable of displaying multiple and single page document formats like PDF and Postscript.
- Engrampa (1.8.1) is an archive manager. This means that you can create and modify archives; view the content of an archive; view and modify a file contained in the archive; extract files from the archive.
- MATE control center (1.8.3) is MATE's main interface for configuration of various aspects of your desktop.
The objective, for openSUSE, is to provide the same experience users had when they used GNOME under openSUSE 11.4, with the main-menu and the Sonar theme.
Enlightenment
Packaging Changes
The enlightenment packaging sees some major changes since openSUSE 13.1, Most notably we have updated to enlightenment e19 which has resulted in some packaging changes as the old package was called e17. The new package is called enlightenment with the old enlightenment package being renamed to e16. As in some minor e17 features have been removed in the creation of e19 enlightenment e17 is still available in the e17 package
| Package Name | Enlightenment version |
|---|---|
| enlightenment | e19 |
| e17 | e17 |
| e16 | e16 |
New Features
- New Dark and Light themes
- New Dock and Tiling profiles
- Package kit module integrated with YaST
- Live previews in pager
- Much improved taskbar (IBar)
- Music Control module
Terminology
WE are shipping terminology 0.6.1 as part of openSUSE 13.2 which also contains many new features with, Splits, Tabs and More complete configuration dialogs
Other Free Desktops
Window Managers
Graphics
Input Methods
New and updated applications
General utilities
Browsers
Graphics and multimedia
- VDR - The Video Disk Recorder is now version 2 (prior it was 1.6) which fully supports HDTV and cards for DVB-S2 and DVB-T2.
Office suites and Personal information applications
Systems Administration
Scientific
- OS1320 Science Stellarium.png
Stellarium showing the night sky
- OS1320 Science Scilab.png
Scilab in action
- OS1320 Science Veusz.png
Veusz, a GUI plotting software
- OS1320 Science wxMaxima.png
wxMaxima running Maxima
GNU Radio
GNU Radio (latest upstream version 3.7.5) is a free software development toolkit that provides signal processing blocks to implement software-defined radios and signal processing systems. It can be used with external RF hardware to create software-defined radios, or without hardware in a simulation-like environment. It is widely used in hobbyist, academic, and commercial environments to support both wireless communications research and real-world radio systems.
Scilab
For the first time, Scilab (latest upstream version 5.5.1) , the MATLAB-compatible numerical computation application, is available from the default repository. See the news item here for more details.
Packages for high-energy physics computation
A number of applications and libraries very commonly used for high-energy particle physics computation and simulation has been added to the default openSUSE 13.2 repository (these were available for openSUSE 13.1 and earlier through the addon science repository). These include:
- Pythia (8.186): A widely used event generator for collisions at high energies between elementary particles
- SHERPA-MC (2.1.1): A Monte Carlo event generator for the Simulation of High-Energy Reactions of PArticles
- Rivet (2.1.2): A toolkit for validation of Monte Carlo event generators
- YODA (1.2.1): A lightweight common system for MC event generator validation analyses
- HepMC (2.06.09): An object oriented event record written in C++ for High Energy Physics Monte Carlo Generators
- FastJet (3.0.6): Jet finding in pp and e+e- collisions
- Herwig++ (2.7.1): An object oriented particle physics event generator, written in C++
- LHAPDF (6.1.4): A unified and easy to use interface to modern PDF sets
- Rk (1.5): A C++ library implementation of several basic geometric entities and transformations for relativistic kinematics
- Cadabra (1.33): Computer algebra system (CAS) designed specifically for the solution of problems encountered in field theory
Armadillo
Armadillo, a popular linear algebra library in C++ was updated to version 4.450.4, a major feature upgrade to version 3.930.3 available with openSUSE 13.1.
MathGL
MathGL has been updated to version 2.3 (2.1 in openSUSE:13.1).
Maxima and wxMaxima
The symbolic computation application Maxima has been updated to the latest upstream version 5.34.1 (5.31.3 in openSUSE:13.1). The wxWidgets-based frontend to maxima, wxMaxima, was updated to version 14.09.0 (13.04.2 in openSUSE 13.1).
Octave
GNU Octave, a high-level interpreted language primarily intended for numerical computations, has been updated to version 3.8.2 (3.6.4 in openSUSE 13.1). This is a major feature upgrade, in particular, adding a new (as yet experimental) GUI support and direct OpenGL support among many other new features. See here for a summary.
PLplot
The plotting library PLplot with bindings for a large number of programming languages has been updated to version 5.10.0 (5.9.9 in openSUSE 13.1).
Stellarium
The popular planetarium simulator Stellarium sees a major update to version 0.13.0 (0.12.4 in openSUSE 13.1). It is now built upon the QT5 toolkit and includes a bunch of new features.
Texmaker
Texmaker was updated to version 4.3 (4.0.4 in openSUSE:13.1). This update adds scripting support, a new wizard for beamer presentations, LuaLaTeX support, and a visual diff view for the source viewer.
Veusz
The GUI plotting software Veusz has been updated to version 1.21.1 (1.18 in openSUSE 13.1). Apart from a number of new features and bug-fixes, it is now available in both python 2 and python 3 flavours (try python3-veusz) from the default repository.
Vtk and Paraview
The large data analysis and visualization applications Vtk and Paraview have been updated to their latest upstream versions 6.1.0 (6.0.0 in 13.1) and 4.2.0 (4.0.1 in 13.1) respectively. VTK 6.1.0 fixes bugs and adds features on top of the more modular code structure of version 6.0. With about 170 issues resolved, the updated Paraview includes several bug fixes and feature enhancements, notably:
- A Redesigned Color Map Editor panel
- Enhancements to Find Data dialog
- Enhancements for interactions with Plots
- Support for Python-based views
- Updates to ParaViewWeb
Financial
GNU Cash
GNU Cash 2.6 comes with many new features most notably:
- Jplot support to give graphical reports a more professional look
- Preconfigured report management system
- Export reports directly to PDF
- Account colors to help with organization
Web Stack
MySQL
httpd
Cloud
Development tools, IDEs, toolchain
IDEs and compilers
KDevelop 4.7
For the users who are also developers, the distribution offers the latest version of the fully featured IDE KDevelop, the last of the versions based on the 4.x KDE development platform. In addition to C++, there are plugins available which extend its support for additional languages such as PHP or Python.
Languages and Libraries
Security
AppArmor 2.9 contains the new python-based tools developed during GSoC 2013, including the new aa-mergeprof to merge multiple sets of profiles, and aa-cleanprof to remove superfluous rules from a profile.
The mod_apparmor apache module now uses the vhost name as a default hat name, if no other name is defined (see mod_apparmor(8) for details).
AppArmor 2.9 also contains some new rule types to mediate sockets, ptrace, signals and dbus. Note that those rules are not yet supported by the openSUSE kernel and dbus, so they're just ignored.
Of course the new version also contains the usual bunch of profile updates, bugfixes etc.
Games
- pink pony now ships with openSUSE