Features
openSUSE 12.3 – Free, Open and Awesome
Beste gebruikers, vrijwilligers, fans en vrienden! De nieuwste openSUSE is klaar voor u. Na zes maanden van hard werken, brengen we u het beste dat Vrije software te bieden heeft met een uniek Groen sausje - stabiel, vriendelijk en leuk.
Meer details over openSUSE 12.3
De volgende tekst behandelt veel details over alle nieuwe ontwikkelingen in deze openSUSE uitgave. Teveel informatie? Lees dan Feature highlights.
Inhoud
Onder de motorkap
Onze infrastructuur is ge-upgrade waarbij nieuwe technologieën verder zijn geïntegreerd. Dit heeft geleid tot toegenomen prestaties, verbeterde hardware ondersteuning en een verbeterde configuratie.
Linux 3.7
Deze uitgave heeft Linux Kernel 3.7, terwijl openSUSE 12.2 nog kernel 3.4 had. Nieuwe en verbeterde functies omvatten:
- Alle bestandssystemen profiteren van de verbeteringen op het gebied van RAID, die een snellere opbouw van een raid systeem mogelijk maken. Er is RAID 10 ondersteuning voor de device mapper en functionaliteit voor SSD's is verwijderd. Om energie te sparen is het interface voor het kernel bestandssysteem aangepast door een daemon te verwijderen die dit subsysteem iedere 5 seconden activeerde. De verbeteringen aan het algemene bestandssysteem omvatten:
- Metadata kan nu kleine bestanden bevatten (lezen en schrijven gaat sneller en het bespaart ook wat opslagruimte) en met een checksum worden gecontroleerd om zijn bestandsintegriteit te beschermen in Ext4. Er is nu ook verbeterde quota ondersteuning en sneller overschrijven van bestanden, alsmede van omvang veranderen van schijf volumes (zelfs als die groter zijn dan 16TB).
- Btrfs is verbeterd met I/O faalcijfers, subvolume quota's, quota groepen, snapshot diffs, snellere fsync, sneller lezen en schrijven voor VM images en de mogelijkheid om per bestand copy-on-write uit te schakelen.
- XFS heeft nu een betere snelheid en een lagere latency, verbeterde ondersteuning voor grote directory block omvang en nog meer kleinere functies en verbeteringen.
| Dit artikel is nog maar gedeeltelijk vertaald. Als u mee wilt helpen met vertalen lees dan Wiki vertalen naar het Nederlands. |
- userspace probes for performance profiling with tools like Systemtap or perf and a new "perf trace" tool modeled after strace.
- Many improvements to networking. The TCP protocol saw performance work with support for TCP "Fast Open" mode for both clients and servers and TCP Early Retransmit (RFC 5827) as well as inclusion of the a "TCP small queues" feature and a new network queue management algorithm designed to fight bufferbloat. Other low-level protocol enhancements include support for checkpointing and restoring TCP connections and a new tunneling protocol that allows to transfer Layer 2 Ethernet packets over UDP. New is experimental SMBv2 protocol support as well as stable NFS 4.1 and parallel NFS support and the ability to have safe swapping over NFS/NBD.
- The kernel now allows for Android-style opportunistic suspend (‘wakelocks’) and has support for hybrid suspend to disk and memory at the same time which removes the risk of data loss if you run out of battery whilst suspended-to-ram. (Do these features get used by userspace/the desktops? If not, we should not talk about these features. Who can confirm this?)
- In the security area we see added support for signed kernel modules, the Intel "supervisor mode access prevention" (SMAP) security feature, VFIO, which allows safe access from guest drivers to bare-metal host devices and a sandboxing mechanism that allows to filters syscalls. It has also become possible to tell the kernel to not follow hard- and softlinks in certain directories, when those links point somewhere higher up the directory tree, blocking a common way for crackers to increase their privileges on a system. Last but not least, the kernel has gotten better at gathering entropy, collecting it from previously unused sources like MAC addresses, DMI data and USB hardware information.
- Other improvements include the ability to do SCSI over Firewire and USB, aggressive SATA device sleep for SSD and HD drive power saving and support for the PCIe “d3cold” power state.
- As always there have been many improvements in hardware support, performance and stability in the graphics drivers, storage, webcam, audio, wifi, and other subsystems. Changes include code for handling the upcoming Intel Haswell graphics core, major changes resulting in a faster and more stable Nouveau NVidia driver with support for newer video cards, improved NFC support, and specific drivers for a large number of laptops.
(overview possible thanks to kernelnewbies.org and The awesome H online kernel logs)
ARM, UEFI and Secure Boot
- This release delivers proper UEFI support for x86_64 hardware and experimental support for Secure Boot enabled hardware. See this wiki page for more information and this blog for background on what solutions we have chosen.
- The openSUSE ARM team has released official openSUSE 12.3 ARMv7 images and experimental ARM 64bit images are already available on the AArch64 page.
systemd
openSUSE 12.3 completes the move to systemd (updated to version 195), and has dropped SysV init. Many packages in the core system have gotten patches and improvements to work better with this next generation init system. Other changes:
- systemd now controls system hibernate and suspend, and power, sleep and lid switch buttons. This means that even when not logged in, closing the lid will put your system to sleep, preventing your laptop from overheating when you failed to notice you were not logged in. this needs to be tested to see if it works. If so, please remove this sentence.
- systemd-delta lets you see how configuration files have changed since installation.
- The “.service” filename suffix may be omitted by referring to systemd services in tools such as systemctl, journalctl..
- The systemd GTK configuration tool has been split off into the systemd-ui package.
journal
Systemd now aggregates all services’ output (including syslog entries) to a journal. This output will by default be forwarded to your standard system logger implementation (rsyslog, syslog-ng).
- The journal can be accessed in a human-readable format using journalctl. Try
journalctl -f! - By installing the systemd-logger package, replacing rsyslog, journal entries will be written to disk natively in a cryptographically protected binary format.
- There is a journal gateway daemon to access the journal via HTTP and JSON. Info here. This gateway is not enabled by default.
Other features and changes
- PulseAudio was upgraded from 1.1 to version 3, which adds support for Bluetooth audio sources, provides better AD2P audio quality, virtual surround sound mode, and support for more noise cancellation modes. There is also UCM support, runtime editable LADSPA filter parameters, configurable device latency offset and lots of infrastructure improvements.
- The btrfs filesystem snapshot tool ‘Snapper’ leaps from 0.0.11 to version 0.1.1, now allows non-root users to make snapshots [1] and experimental support for LVM thin-provisioned snapshots [2].
- The latest Mesa 9.0 brings OpenGL 3.1 as well as many other performance improvements and bugfixes.
- In the package management area, version 1.8.9 of zypper now shows package installation progress. The PackageKit backend for zypper was rewritten, giving a much improved package management experience with the cross-distribution GUI tools.
- sshd now has stronger sandboxing to protect against hacking attempts
- shadow replaces our old pwdutils fork of shadow. Its changes were merged back upstream
- Standard Linux PAM modules like pam_unix.so and pam_cracklib.so are now used by default on new installations, as they now offer the features of the SUSE-developed pam_unix2.so and pam_pwcheck.so.
- selinux-policy was updated to 2.20120725
Free Desktops
openSUSE is unique among the major Linux distributions in delivering all major Free Desktops on an equal footing: officially developed and supported. These include GNOME, KDE’s Plasma Desktop (the default desktop) and Plasma Netbook, Xfce, LXDE, KDE 3 and the brand new E17. As usual, this release introduces nice new artwork from boot up to application splashes. KDE in particular got a nice, dark new theme for the Plasma Workspace.
Plasma Desktop
The update to KDE’s workspace brings many refinements to openSUSE. For this release the openSUSE KDE team worked to bring a nice, dark theme to the desktop. If you like a dark theme for your applications as well, you can select the openSUSE dark theme from the colors section in the Application Appearance settings. The included standard 'Obsidian Coast' is another good color scheme worth trying. For people who prefer the default Plasma look and feel, an improved Air theme is available as well. Below an overview of the major feature changes.
- Version 4.10 of the Plasma Desktop includes many widgets ported to the new QML technology. While not bringing new features, this improves the behavior, performance and stability of the desktop components.
- In the window management area, it is now possible to easily download scripts with additional functionality and effects for KWin. By default, a new script for animating the maximizing of windows is included. Other improvements in KWin include openGL support in most virtual machines and the window manager now has per-monitor support for color management.
- A major new feature is support for a top-screen- or title bar button for the menu. By enabling one of these options under Application Appearance-Style-Finetuning in Systemsettings, the menu will disappear from the application. It will now be available as a new button on the window decoration (location of which is of course configurable) or in a automatically hiding menu on top of the screen (or just below the top screen panel), popping up when you move your mouse there.
- The file manager part of Plasma Desktop, Dolphin, received vast improvements in performance on large folders and meta-data based grouping capabilities and smarter search options have been added.
- Metadata handling has been improved in other area’s too, with faster indexing that interferes less with daily work. The introduction of Nepomuk Cleaner offers a simple tool for cleaning up the semantic metadata storage. It cleans up legacy and invalid data and merge duplicate entries, speeding up handling of email and searching of files significantly. Running it can take considerable time (up to a day) but is highly recommended.
- Printer management has been improved with the inclusion of the new Print Manager. A Plasma applet shows printers and lets you control queued jobs while the System Settings screen lets you add, remove and configure printers. The new Printer Wizard is much smarter than the previous one and the new Print Manager works much better with the latest CUPS.
- The Apper update manager v 0.8 should no longer create blocking issues with the zypper commandline and GUI package managers. New is a plasmoid for handling updates. It is not included by default but you can download it from the repositories. Apper will also show and describe untrusted packages and can automatically download packages in preparation for review. Notifications are properly integrated, performance and GUI have been improved and many bugs were squashed.
- Bluetooth integration in the workspace received several improvements in the behavior and the user interface, making more reliable connections and less interruptions possible.
GNOME Shell
This is the third openSUSE release featuring GNOME 3. Highlights for this release include:
- Big improvements to notifications, including a redesigned Message Tray, smarter notifications, and other tweaks and refinements. The items in the tray are also bigger, clearer, and don't move around, making them easier to use.
- An enhanced Activities Overview with an improved layout. One change is the way that application launchers are reached. In previous versions, you used the application tab in the top-left to access your applications. This has been replaced with a new grid button that is located in the dash.
- A greatly enhanced Files application (also known as Nautilus), with functional file search, a new Recent location, redesigned interface and lots of bug fixes and handy new features.
- Integrated Input Sources, which makes inputting different character sets (eg. Japanese or Chinese) fast and easy.
- Accessibility on demand, meaning that universal access features like the Orca screen reader can be enabled with the push of a button.
- A new Lock Screen. This provides an attractive view when the device is locked, plus handy functionality like media controls. The lock screen means that you can see what is happening while your computer is locked, and it allows you to get a summary of what has been happening while you have been away. It also means that you can easily change the volume, skip a track or pause your music without having to enter a password.
There are many other enhancements in GNOME 3.6, including Online Accounts support for Microsoft Exchange and Windows Live (SkyDrive access via Documents application) and much improved System Settings (it includes larger icons and a better layout, all the icons are now displayed whenever possible). Airplane Mode now switches off all radios, including Bluetooth. Many of the basic GNOME tools have also received improvements, including Disk Usage Analyzer, Disks and the Font Viewer. Find more details in the release notes
Xfce
The Xfce desktop has been updated to the latest bugfix releases and there have been major updates of the Thunar file manager and Terminal which has been renamed to xfce4-terminal. Thunar 1.6.0 introduces tab support, improved bookmark handling (including easily adding remote bookmarks) and features several UI improvements, a check for free space before copying starts, and extensive performance improvements. xfce4-terminal 0.6.0 has been modernized and received a number of bugfixes and, most importantly, now supports a Quake-style drop-down mode which keeps a running terminal around that can be quickly accessed through a keyboard shortcut.
Other Free Desktop and window managers
With E17 as new Desktop Environment and two new window managers (awesome and Sawfish) this openSUSE release has lots to offer for those not big fans of the traditional desktops.
awesome Window Manager
New in openSUSE 12.3 is awesome, a highly configurable, next generation framework window manager for X. It is very fast and extensible. It is primarily targeted at power users, developers and any people dealing with every day computing tasks and who want to have fine-grained control over their graphical environment and have the skills to make that happen.
A window manager is probably one of the most used software in your day-to-day tasks, with your Web browser, mail reader and text editor. Power users and programmers have a big range of choice between several tools for these day-to-day tasks. Some are heavily extensible and configurable.
awesome tries to complete these tools with what we miss: an extensible, highly configurable window manager. To achieve this goal, awesome has been designed as a framework window manager. It's extremely fast, small, dynamic and heavily extensible using the Lua programming language. Essentially, the idea is that you build your own window manager, offering exactly the functionality you desire.
awesome provides an easily usable and very-well documented API to configure and define the behavior of your window manager.
Sawfish Window Manager
Sawfish is an extensible window manager using a Lisp-based scripting language. Its policy is very minimal compared to most window managers. Its aim is simply to manage windows in the most flexible and attractive manner possible. All high-level WM functions are implemented in Lisp for future extensibility or redefinition. These are some of the features that set Sawfish apart from other window managers:
- Powerful key-binding: Virtually every function provided by Sawfish can be bound to keys (or mouse buttons).
- Event hooking: For many events (moving windows etc.) you can customize the way Sawfish will respond.
- Window matching: When windows are created you can match them to a set of rules and automatically perform actions on them.
- Flexible theming: Sawfish allows for very different themes to be created and a variety of third-party themes are readily available.
Sawfish detects your desktop environment and integrates to your environment whether you are using KDE or Gnome or LXDE or XFCE or Mate.
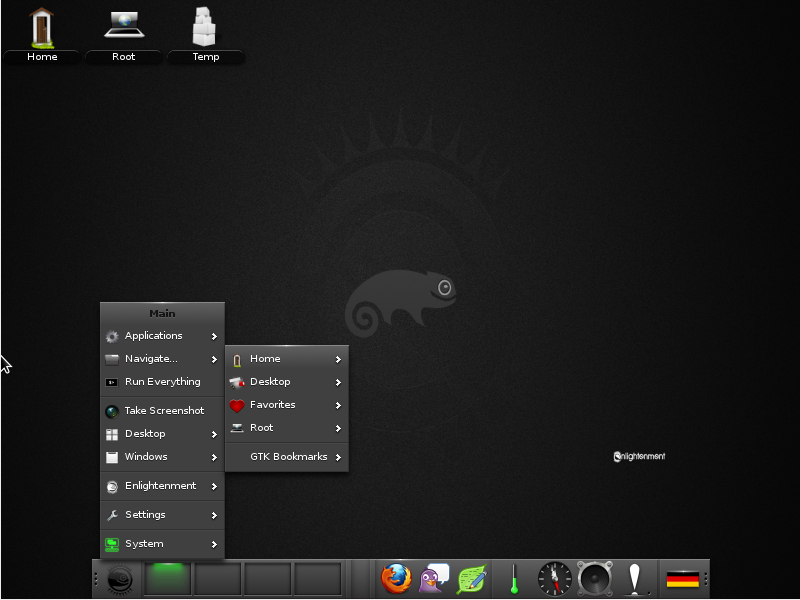
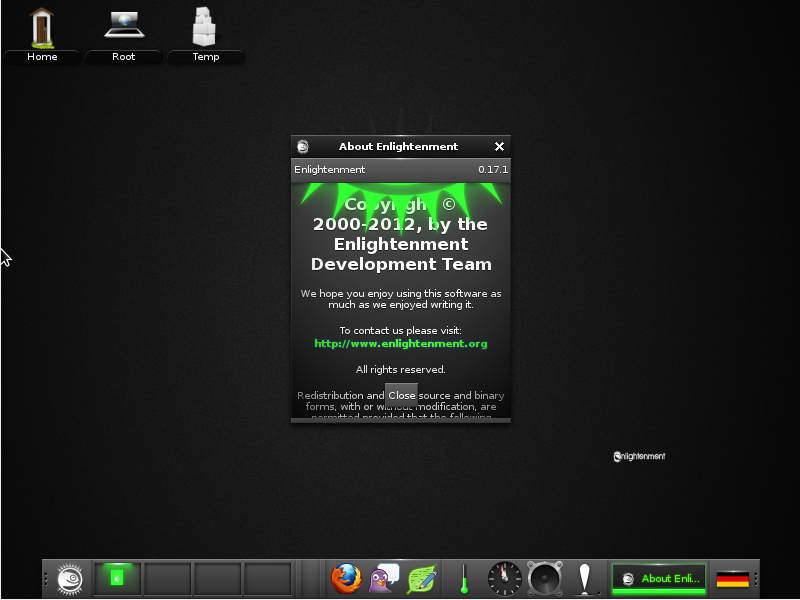
Enlightenment 17
As Enlightenment 0.17 or (E17) was finally released, we are happy to make it available. It is a complete rewrite on DR16 and was designed to be a full-fledged desktop shell, based on the new Enlightenment Foundation Libraries (EFL). Check the Enlightenment Portal page for more information.
Others
PCMan, the filemanager of the LXDE lightweight desktop, is included with a new version. The 1.1 release brings some UI improvements like disabling items which cannot act (like 'copy' on selected items) in the menu and toolbar, the option to 'treat backup files as hidden', the ability to change the columns in the Detailed List View and search engine support. Underlying improvements were made to stability and performance, as well as bringing new support for unmounting removable media without ejecting them and some other small changes.
Another part of this release is WindowMaker 0.95 which introduces some changes in the preferences and the addition of a new "Center" placement strategy, support for _NET_FRAME_EXTENTS and the removal of CPP dependency to process menu files.
New Input method
All desktops now have access to Mozc, a Japanese input method engine developed by Google. It is becoming a de facto standard in Linux community because it provides more precise conversion and it seems that the previous standard engine, Anthy, is not maintained anymore. Zinnia and zinnia-tomoe provide hand-writing recognition for mozc.
The package of Mozc has been incubated for more than a year in the M17N project on the Open Build Service. It has received a lot of testing and many Japanese users have been installing it by hand, so it was time to move this to openSUSE proper!
Link to video for Chinese users: here
TeXLive
LaTeX lovers will appreciate that TeXLive 2012 had been splitted into several packages to have a highly modularized TeX typesetting system. The split was done accordingly to the upstream known packages of TeXLive.
These package are grouped into
- Filesystem (FHS/TDS), infra structure, collection and scheme packages all noarch. The collection and scheme packages are only place holders for dependencies, that they require the
- noarch packages providing specifiy formats like latex, fonts, styles, and documentation. Those packages do require the
- binary packages providing the programs like the engines pdftex, dvips, xdvi, xetex, and much more
the noarch packages for formats, styles, and engines do provide the files as virtual dependencies. That is the e.g. texlive-latex does provide
`tex(alltt.sty)' upto `tex(tracefnt.sty)' and `tex(article.cls)' upto `tex(slides.cls)' and `tex(omlcmm.fd)' upto `tex(ullasy.fd)' and much more
if something is missed by LaTeX with e.g.
! LaTeX Error: File `multirow.sty' not found.
or
! Font U/pzd/m/n/10=pzdr at 10.0pt not loadable: Metric (TFM) file not found.
then this can be resolved by the commands:
The project URL for this is here with the download repositories here.
New and updated applications
Audio, Video and Photo handling
The latest version of Linux’ most popular music player Amarok 2.7 brings a wide variety of fixes and improvements. A list of major changes:
- Track dragging support in Unique Tracks tab of the Synchronize Statistics action; allows you to do a "diff" between collections and transfer missing tracks.
- Amarok now scrobbles tracks in streams if the stream correctly updates meta-data.
- When scrobbling to Last.fm, Amarok announces suggested tag corrections (configurable).
- Ability to scrobble recently played tracks from iPod to Last.fm.
- Synchronization of labels and rating between Last.fm and Amarok collections; play count can be synchronized one-way from Last.fm to Amarok.
- Statistics synchronization between collections, supports rating, first / last played time, play count and labels.
- Mark downloaded podcast episodes to keep, even when purge is enabled.
- Nepomuk plugin: Play and manage tracks using the Nepomuk database.
- Amazon store: It is now possible to add items to your shopping cart using Amarok:
- Amazon store: Use the context info applet to show further infos about a selected item.
- Amazon store: We now ship a utility to handle downloads from Amazon.
rhythmbox 2.98 brings a host of smaller and larger improvements:
- New dialog for importing music into the library
- New audio CD metadata lookup library, replacing libmusicbrainz
- Improved transitions between album art images
- Nautilus cluebar buttons now result in the right source being selected
- Update notification buttons when playback state changes
- Search musicbrainz for album art by album and artist name
- Love/ban buttons visible in last.fm/libre.fm sources
Audioplayer Banshee 2.6 is the culmination of six months' work by 15 developers, 30 translators and dozens of bug reporters and testers. It adds device scrobbling support for LastFM, file management options are now specific to each source and the "Copy files when importing" and "Update file and folder names" settings can now be set independently for Music and Videos.
Totem Movieplayer got renamed to ‘Videos’ and hides its titlebar when maximized. The menus have been cleaned up, drag and drop in the playlist was improved, DVDs and other optical media are listed with Grilo and connection speed preferences got removed. There is a number of new nice animations and variable rate playback. Visualisations are now off by default and the plugins got improvements with a better search sidebar and a new recent-files handling plugin.
This release of audio editor Audacity 2.0.2 is mostly a bugfix release, with a significant bug that caused clicks on split lines having been fixed. But there are also improvements to several toolbars and to some Nyquist effects, keyboard shortcuts can now be allocated to effects and Nyquist plug-ins can be added to Chains.
The Blender 2.64 3D/video editor release was focused on integrating and stabilizing the long awaited BMesh modelling system, which has full support for N-sided polygons and many new modelling tools. New tools include Dissolve, Inset, Bridge, Vertex Slide, Vertex Connect, Bevel, and improved versions of Knife, Subdivide and Rip. see more here
Digikam 3.0 brings a large number of improvements to Linux’ most powerful Photo Management application. A list of some of these features:
- Improvements to batch processing
- new actions supported: change image sizes, crop, Gamma factor
- can now handle several folders at once
- multi-threading in batch manager
- improved tool handling, including saving, importing and loading of chains of tools
- more flexible placement of files in folder hierarchy
- new video slideshow generator
- Much improved Camera user interface
- Video metadata support
- Automatic noise reduction settings
- better Presentation View
- integrated UPnP/DLNA via plugin
- Geolocation enhancements
- include exif and IPTC data in html gallery export
- import pipelines EXIF autorotation
- new subtag search
- much, much more
The updated libraw library supports a number of new cameras including the Canon 5D Mark III, G1 X, 1D X and Powershot SX200; Nikon D4,D800/D800E and D3200; Fuji X-S1 and HS30EXR; Casio EX-Z8; Olympus E-M5; Panasonic GF5; Sony NEX-F3, SLT-A37 and SLT-A57 and the Samsung NX20 and NX210.
Gwenview, KDE's image viewer, features improved thumbnail handling and generation as well as Activity support. It supports color correction of JPG and PNG files, working with KWin to adjust to the color profiles of different monitors, allowing for consistent color representation of photos and graphics. The Gwenview image importer now works recursively, showing all images available for display below, as well as within, a specified folder.
Personal Information Management and Chat
In the PIM area are applications handling email, chat and other communication duties. Many of these received significant improvements in this release.
Claws Mail has been updated to 3.9. This little GTK email client and news reader is known for being fast, extensible and easy to configure. It adds IMAP server side search and several speed-ups and optimizations.
Evolution 3.6 modifies the preferences and contact editor for small screens, allows you to save events, memos and tasks from the File menu and lets you re-configure already configured systems with the Assistant. Evolution no longer uses GConf but stores its account data in plain text files. The mail formatter received a rewrite and a better highlighter. The search folder can now update automatically and local contact photos are displayed in the image chooser for the contact editor. Also new is spell checking for the ‘Summary’ in Events, Tasks and the Memo editors.
KDE's PIM application suite Kontact has gotten many bugfixes and improvements. Substantial work with the search backend has vastly improved email indexing and retrieval, delivering more responsive applications with lower resource usage. Feature additions and improvements include:
- KMail has a new ability to automatically resize images attached to emails, configurable in KMail's settings.
- The quick search bar above the mail list now searches also in the full bodies of emails.
- KMail introduces Text Autocorrection, including word replacement and capitalize the first letter of a sentence. The settings and word lists are shared with Calligra Words and are configurable.
- HTML composer support has been expanded: tables can be inserted, with control over rows and columns as well as the ability to merge cells. Defined sizes for images are now also supported, as is the ability to insert html code directly .
- The 'plain text' companion to HTML emails was also improved, with HTML tags convertible to plain text equivalents.
- The import wizard gained support for importing settings from Opera, settings and data from Claws Mail and Balsa, and tags from Thunderbird and Claws Mail.
- Other improvements to KMail include: opening recent files in the composer, adding new Contacts directly from KMail and attaching vcards to emails.
The SoftPhone, Video Conferencing and Instant Messenger application Ekiga 4.0 introduces a major ovarhaul of the main window, a new pulse audio plugin (in ptlib), New audio codecs: SILK (used by skype), G.722.1 (aka Siren 7), G.722.2 (aka GSM-AMR Wide band) , H.323 gatekeeper support, call auto-answer and support for handling multipe video streams (H.239).
The release of the chat application Empathy 3.6 Improves GNOME Online Account integration. This chat application is deeply embedded in the GNOME Shell and received several other minor improvements.
Text editor Gedit 3.6 has updated GtkAssistant support, an extensive new snippet collection for docbook and File Browser side panel improvements.
In the office
The latest stable LibreOffice 3.6 release brings again a large number of additions and improvements such as:
- General: PDF export with Watermark option; allow editing of read-only documents; performance improvements for Calc and Writer (document import, spreadsheet operations)
- Writer: word count in status bar; improved auto format options; improved label and business card support
- Calc: color scales and data bars; sort option in autofilter menu; merge cells using the cell context menu; CSV file import and export improvements; new formula options page with calculation settings
- Draw: Corel Draw import
- Impress: wide-screen format for slides, improved detection of external display
Version 4.0 of LibreOffice did not make it in time for openSUSE 12.3 but is available on software.opensuse.org.
openSUSE 12.3 comes with Calligra 2.5, a very complete productivity and creativity suite of applications.
- In the productivity area, the word processor Words continues to focus on students or academic users. There is improved editing of tables and dragging of text as well as enhancements in the bibliography tools. Spreadsheet application Sheets has a new stand-alone docker for the cell editor and a new cell tool window with formatting controls. Kexi, the database application has a full-screen mode, new form elements and widgets.
- In the artistic department, Free Software’s premiere drawing suite Krita introduces a new compositions docker for movie storyboard generations, textured painting, improved canvas handling and a large number of performance improvements.
- All Calligra applications benefit from an improved autosave system, user profiles, improved charts component, better shape connection and various new effects for images.
Version 2.6 of Calligra was released just too recent to be included in openSUSE 12.3 but it will be available on short notice on software.opensuse.org.
PDF viewer Evince 3.6 introduces offline help courtesy of Yelp, the ability to inhibit the screensaver, find options to the search bar and preserves file metadata upon saving a copy.
Okular Document viewer introduces new features including a technique called tiled rendering which allows the viewer to zoom in further and faster while reducing memory consumption compared to previous versions. The embedded video feature has been improved. Editing and creating annotations in Okular has become more user-friendly with the introduction of high precision QTabletEvents. Now a tablet behaves exactly like a mouse except when creating an annotation. With this task, the high precision position of the QTabletEvent is used, so free-hand annotations are smoother. A new feature allows easy history navigation, which can now be accessed by forward and back mouse buttons.
Calibre 0.9 brings a complete rewrite of the PDF Output engine, to support links and fix various bugs. It can show disabled device plugins in Preferences->Ignored Devices, the Get Books tool works better with Smashwords, Google books and B&N stores and adds the Nook UK store. There is a ‘clear ratings’ button for the edit metadata dialog and a new mass storage driver for rockhip based android smart phones.
Scribus 1.4.2 is mostly a bugfix release, it also adds an often requested feature, namely true cross-platform spellchecking. Until Scribus 1.4.1, the spellchecker worked only on Linux and UNIX systems, including manually built versions on Mac OS X. As of version 1.4.2, Scribus provides a modern spellchecker, similar to LibreOffice and based on Hunspell, which should be easily portable across all supported platforms. Scribus 1.4.2 will detect existing dictionaries already installed by hunspell packages or LibreOffice, on the system it has been installed onto. Additional dictionaries are downloadable directly from within the Scribus Preferences via freedesktop.org. The spellchecker now also works within the Story Editor.
openSUSE 12.3 and the web
openSUSE always comes with the latest latest Mozilla Firefox version (19 at the time of release), part of our updates. Likewise, openSUSE always offers the latest Chromium from Google.
The GNOME webbrowser Epiphany 3.6 now integrates the app menu into the gear menu if the system has no global application menus and offers F10 as shortcut to the gear menu. Restoring the last session on startup is now default, the URL entry layout has been improved and a long click or right click on the back and forward buttons gives you a list of earlier visited sites.
Rekonq got updated to version 2.0. Features in this release include a "web-app" mode, inline spell checking, a new incognito mode similar to Google's Chrome, support for pinning tabs, an improved error page, and various other enhancements.
KTorrent is updated to version 4.3.1. Major changes:
- Sort by total leechers and seeders, if connected seeders and leechers is equal
- Add support for magnet links in the syndication plugin
- Add search line to download order dialog
- Add move top and bottom option to download order dialog
- Add support for removable storage
Feed Reader Liferea 1.8.12 adds Google Plus and Instapaper.com to the Social Bookmarking Sites.
Games and Educational Applications
The ARAnyM Atari emulator got a new precise FPU emulation core and a fully working NF USB. It also brings GEM <-> Host clipboard interconnection and middle mouse click for input un-grab.
A new game part of the KDE Games suite is included with this release. Picmi is a single player logic-based puzzle game. The object of the game is to color cells according to numbers given at the side of the board in order to complete a hidden pattern or picture. Picmi includes two game modes—random puzzles are generated according to the selected difficulty settings or the included preset puzzles.
Other KDE Games have been improved, including the ability to print puzzles from KSudoku so they can be used away from the computer. KGoldrunner was rewritten based on the new KDEGames libraries; gameplay and UI are the same, but the game is prettier and smoother. KJumpingCube now allows adjusting the speed of moves and animates multi-stage moves to make them easier to understand. The UI has been improved and you can now choose which one you'd like to play against: Kepler or Newton. Smaller boards offer simplified playing styles. Pairs gained a theme editor.
The Rocs Graph Theory IDE, a educational application part of the KDE Education suite, has a much improved user interface and configuration dialog to make it easier to use. There is also new support for TGF, DOT/Graphvis (import/export) and TikZ/PGF (export only) files.
Also part of the EDU suite is Marble, the virtual globe for Linux. For this release, Marble moves forward into the area of Space Science. The European Space Agency supported work on a visualization of space orbiters around other planets inside the Marble Virtual Globe. As a result, Marble can display the positions and orbit tracks of space missions such as Mars Express, Venus Express and SMART-1. The visualization also includes the positions of the two Mars moons Phobos and Deimos. He also enhanced Marble's display of Earth satellite tracks. A video presents some of the features that have been added.
Another major feature new in Marble is support for the OpenStreetMap Vector format. A video of this feature is available as well. Currently, the default maps in Marble are not vector-enabled yet but other maps can be downloaded easily.
Ktouch, KDE's touch typing tutor has been rewritten. It now features a clean, elegant and vibrant user interface to make learning and practicing touch typing as enjoyable as it can be. The new user interface reduces complexity, and guides the user with color cues and inobtrusive animations. Many new features help improve the overall training experience—a new course editor has built-in quality checks, the user can review progress and identify weaknesses, the overall appearance is attractive and scaled to screen size, hinting and obvious problem solving tips are displayed prominently. See for some screenshots and further information this blog.
For developers
As always, we’ve updated our tool chain with the latest CMake, GCC, git, gtk2 and 3, Java and more. Below you can find an overview of the major changes in this release.
IDEs and tooling
Development tool Anjuta has been upgraded to version 3.6.2, adding ‘make check’ and subdirectories support to the project manager. It also has some improvements to the git integration, showing the Git Tasks dock when the Git dock is active and the Status view as default. There are also new plugins for indentation and language support.
QtCreator 2.6 introduces Kits as a replacements for ‘Targets’ in the 2.5 and earlier releases. Kits generalize the magic which Targets applied on top of the builds, offering settings for which device type to develop for, the sysroot, compiler, debugger, Qt version to use and a few more. This way, code sharing between projects is much easier. Another inclusion in QtCreator 2.6 is experimental Android support from Necessitas and support for QNX/Blackberry devices. Unfortunately, due to a lack of maintenance, Symbian support had to be dropped.
Other improvements include the ability to type e.g. ‘’’fii,txt:123’’’ in Locator to jump directly to that line in that file, fixes to the qrc file editor, highlighting of missing files in the resource editor, C++11 fixes and more.
Glade 3.14, the GNOME/GTK tool to develop user interfaces, brings back to life GtkAssistant support and let you define styles classes. Thanks to a rework of the UI with Glade itself, many small UI improvements are present as well as some larger ones like the new font dialog, the new color chooser and a new GladePreferences dialog.
Kate, the KDE Advanced Text editor got an improved notification system, an optional 'minimap' as scrollbar, a new Project Management plugin, predefined color schemes, improvements to the scripting interface, support for python plugins and much more. A great bugfixing effort reduced the number of open bug reports from 850 to 60. Work was also done to create a new Quick Open functionality and other enhancements. Most of these improvements also benefit applications using Kate Part for text editing, including the lightweight KWrite text editor and KDevelop.
Aside from benefiting from the improvements in its core text editing component provided by Kate, KDevelop 4.4 introduces a new QML based welcome screen. It is shown when no files are open and helps you to get started in an intuitive way. Its code screen offers a list of projects and coding sessions, the debug screen gives you the tools for debugging and optimizing applications and the review area helps you reviewing patches.
There has also been a host of smaller improvements, from cleaning up the templates to CMAKE integration improvements and much more.
The latest monodevelop 3 provides preliminary Android API17 (Jellybean 4.2) support and database extensions.
The powerful Valgrind 3.8 suite of tools for debugging and profiling offers a large number of enhancements. A quick list:
- preliminary support for Android on x86
- support for Intel AVX and AES instructions (only for 64bit code)
- POWER Decimal Floating Point instruction support
- significant changes to malloc support including the option to work with non-libc malloc implementations
- memory leak check performance improvements
- new GDB server monitor commands ‘block_list’ ad ‘who_points_at’
- C++ demangler can work with at least G++ 4.6 binaries
- more scheduling options for threaded code
- and much, much more. See the valgrind website for more information.
New in openSUSE 12.3 is the Fossil Distributed Version Control System, which offers a number of unique features in the DVCS area: distributed wiki, bugzilla and blog functionality; autosync mode to reduce pointless forking and merging; and a build-in web interface. See LWN for more.
GCC has been updated to 4.7.2, bringing in several bugfixes.
openSUSE specific tools
KIWI is the openSUSE operating system image creator, used for generating hard disk images, Live CD’s and USBs, VMware appliances and a large number of other images including the official openSUSE release and the tens of thousands of images on SUSE Studio. This new version brings UEFI support and a load of other improvements. A list of the major changes in KIWI 5.04.37:
- add error condition for architectures that do not support the creation of iso hybrids
- added support for firmware="uefi" attribute. In contrast to the standard firmware="efi" support, kiwi will not create its own efi boot images but uses the shim and the signed bootloader modules as they are provided by the packages.
- added the firmware type 'vboot' to support creation of images for arm based boards using google's chrome OS boot style
- added support for EFI in live ISO images
- added support for software raid into disk based appliances
- added support for the apt-get/dpkg package manager to kiwi
- added support for optional type attribute 'bootfilesystem' which can be one of ext2,ext3,fat16 or fat32 (bnc #788374)
- Added armv5 support
- added support for btrfs seed live ISO images.
- added support for filesystem mount options during image build and later to become stored in the fstab file
openSUSE 12.3 includes the SUSEpaste script - the essential collaborative debugging utility to paste outputs/logs easily to the openSUSE Paste site from the command line.
A new security tool (gpg-offline) has landed in Factory. It is used to check for GPG signatures of upstream tarballs.
The Open Build Service command line client OSC now supports creating and releasing maintenance updates for openSUSE.
Languages and Development Libraries
openSUSE comes with a wide variety of languages. We ship not only python, PHP, Ruby, Go and many more but updated versions and interesting enhancements or modules can always be found on software.opensuse.org, courtesy of the Open Build Service. The major development Platforms like the KDE Platform, the GNOME libraries and the Enlightenment Foundation Libraries are of course also available on openSUSE, and them too, in various versions on OBS.
Languages
Mono 3 supports the new async C# 5.0 as well as some new assemblies: System.Net.Http, System.Threading.Task.Dataflow. Microsoft's open source ASP.NET WebStack is included as well as the Entity Framework and Partial support for Portable Class Libraries. Aside from performance and stability improvements there is also better GDB support for SGenGC internals.
Though Python 2.7.3 remains the default, Python 3.3.0 is now available, bringing a wide range of changes:
- PEP 380, syntax for delegating to a subgenerator ("yield from")
- PEP 393, flexible string representation (doing away with the distinction between "wide" and "narrow" Unicode builds)
- A C implementation of the "decimal" module, with up to 120x speedup for decimal-heavy applications
- The import system (__import__) now based on importlib by default
- The new "lzma" module with LZMA/XZ support
- PEP 397, a Python launcher for Windows
- PEP 405, virtual environment support in core
- PEP 420, namespace package support
- PEP 3151, reworking the OS and IO exception hierarchy
- PEP 3155, qualified name for classes and functions
- PEP 409, suppressing exception context
- PEP 414, explicit Unicode literals to help with porting
- PEP 418, extended platform-independent clocks in the "time" module
- PEP 412, a new key-sharing dictionary implementation that significantly saves memory for object-oriented code
- PEP 362, the function-signature object
- The new "faulthandler" module that helps diagnosing crashes
- The new "unittest.mock" module
- The new "ipaddress" module
- The "sys.implementation" attribute
- A policy framework for the email package, with a provisional (see PEP 411) policy that adds much improved unicode support for email header parsing
- A "collections.ChainMap" class for linking mappings to a single unit
- Wrappers for many more POSIX functions in the "os" and "signal" modules, as well as other useful functions such as "sendfile()"
- Hash randomization, introduced in earlier bugfix releases, is now switched on by default
In total, almost 500 API items are new or improved in Python 3.3. For an even more extensive list of changes in 3.3.0, see this page.
Further in the Python world, Python-qt4 supports Qt 5 now and python-twisted 12.3 brings a number of bugfixes as well as some new features:
- The new -j flag to trial provides a trial runner supporting multiple worker processes on the local machine, for parallel testing.
- twisted.internet.task.react, a new function, provides a simple API for running the reactor until a single asynchronous function completes.
- twisted.protocols.ftp.FTP now handles FEAT and OPTS commands.
- trial now supports specifying a debugger other than pdb with the --debugger command line flag.
- twisted.python.util.runWithWarningsSuppressed has been added; it runs a function with specified warning filters.
- trial's skipping feature is now implemented in a way compatible with the standard library unittest's runner.
- The setup3.py script is now provided to provisionally support building and installing an experimental, incomplete version of Twisted in a Python 3 environment.
- twisted.python.util.FancyStrMixin now supports arbitrary callables to format attribute values.
- Several new methods of twisted.trial.unittest.SynchronousTestCase - `successResultOf`, `failureResultOf`, and `assertNoResult` - have been added to make testing `Deferred`-using code easier.
Ruby and the ruby gems included in openSUSE have mostly seen minor updates to fix security and stability issues or support newer versions of their dependencies.
Haskell is a pure functional programming language and Haskell Platform is a carefully selected set of Haskell libraries. Haskell Platform [3] 2012.4.0.0. ships with ghc [4] 7.4.2.
Steel Bank Common Lisp (SBCL) is an actively developed a high performance Common Lisp compiler. In addition to the compiler and runtime system for ANSI Common Lisp, it provides an interactive environment including a debugger, a statistical profiler, a code coverage tool, and many other extensions. Lisp is a general-purpose, multi-paradigm programming language. It supports a combination of procedural, functional, and object-oriented programming paradigms. As a dynamic programming language, it facilitates evolutionary and incremental software development, with iterative compilation into efficient run-time programs. Previously only clisp was available as the platform in openSUSE
Development platforms and libraries
GTK 3.6 is part of this release. Major new features include:
- GtkSearchEntry: a GtkEntry subclass that is set up to be a search entry
- GtkMenuButton: a button that pops up a menu. The menu can be generated from a GMenu or provided manually
- GtkLevelBar: a new widget for displaying the strength or level of some quantity
- Spin buttons can be oriented vertically
- Text views and entries can display 'selection handles' when used with touch devices
- Theming
- Support for cross-fading and transitions
- Support for CSS animations
- Support for blur shadows
The KDE Development Platform introduces a more comprehensive SDK for Plasma.
- Development tools are brought together into PlasMate and the use of Qt Quick within Plasma continues to expand, making it easier to extend and customize Plasma Workspaces.
- Containments (the area where widgets on desktops and panels are situated) can now be written in QML, making them easy to customize for experiments or special use cases.
- The KWin window manager introduces new scripting interfaces for window effects, behavior and management. A number of example scripts helps potential script writers get started. Find some tutorials here.
opencv 2.4 brings significantly improved and optimized Android and iOS ports and a greatly extended GPU (i.e. CUDA-based) module.
The latest Poppler 0.22 library brings improved PDF rendering, annotation and form improvements, more xhtml-compliant html output and a number of stability fixes.
The Soprano modular RDF storage framework brings a series of code optimizations as well as support for plain SQL queries in the Virtuoso backend, a custom socket implementation which makes it possible to use a single socket accross threads and some more minor fixes and improvements. The zeromq socket library version 3.2 brings many new features and API improvements. A list can be found here
In Cairo 1.12.8, the MSAA compositor was refined in the gl area. In cairo-xlib, SHM transport for image transfers to and from the X server was enabled, offering a notable reduction in rendering latency. Many corner cases in cairo-pdf were fixed, improving opacity groups and font subsetting. In cairo-image, support was added for rendering glyphs to pixman and using that from within cairo, improving glyph throughput for the image backend by a factor of about 4. A few bugs in the glyph rendering code were fixed, along with many other bugs.
Servers and virtualization tools
In the virtualization area, we’ve got updates to the main technologies letting you run other operating systems on openSUSE as guests or use openSUSE as a guest on other systems. For servers, openSUSE updates to the 9.2 release of PostgreSQL and moves to MariaDB, replacing mySQL as default.
Virtualization tools
Virtualbox 4.2 brings support for limiting network IO bandwidth and improved 3D performance to your system as well as better network device support (up to 36 network cards, in combination with an ICH9 chipset configuration). It also introduce new features in GUI like grouping VM and possibility to alter some settings during runtime.
We also ship the 4.2.1 release of Xen
The KVM and Qemu updates to 1.3.0 vastly improved the USB stack with mass storage device and USB3 support as well as MSI/MSI-X support for the XHCI controller. Other goodies:
- QEMU can now use the Linux VFIO driver for guest PCI devices
- New paravirtualized hardware random number generator device
- New block jobs: live block commit (a.k.a. snapshot deletion) and live disk mirroring (a.k.a "storage migration")
- New CPU models: "Haswell" and "Opteron_G5"
- USB redirection now supports live migration
- NBD block devices can now be specified using URI syntax
- QEMU embeds an NBD server, accessible via the monitor
- Improved support for sandboxing using seccomp mode 2
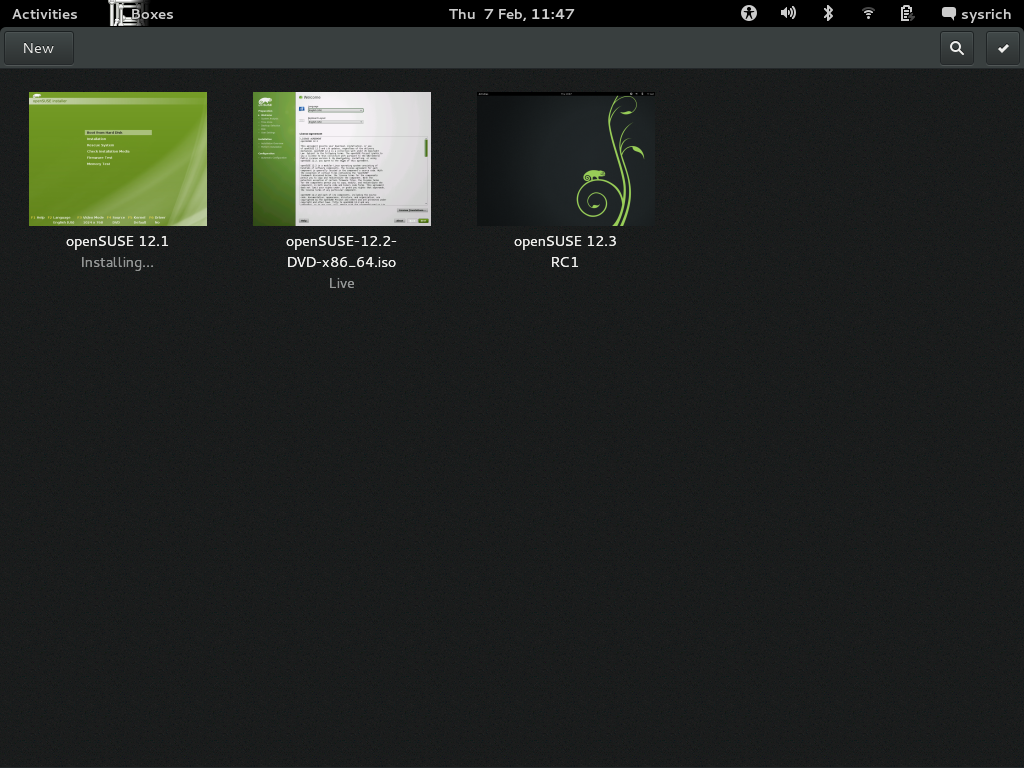
This release includes the first major release of Boxes, an application for using remote systems and virtual machines. It offers a pretty and simple interface for handling any number of connections using Spice as protocol, featuring auto-detection of Virtual Machine format and a variety of other conveniences in a pretty interface.
Server technology and databases
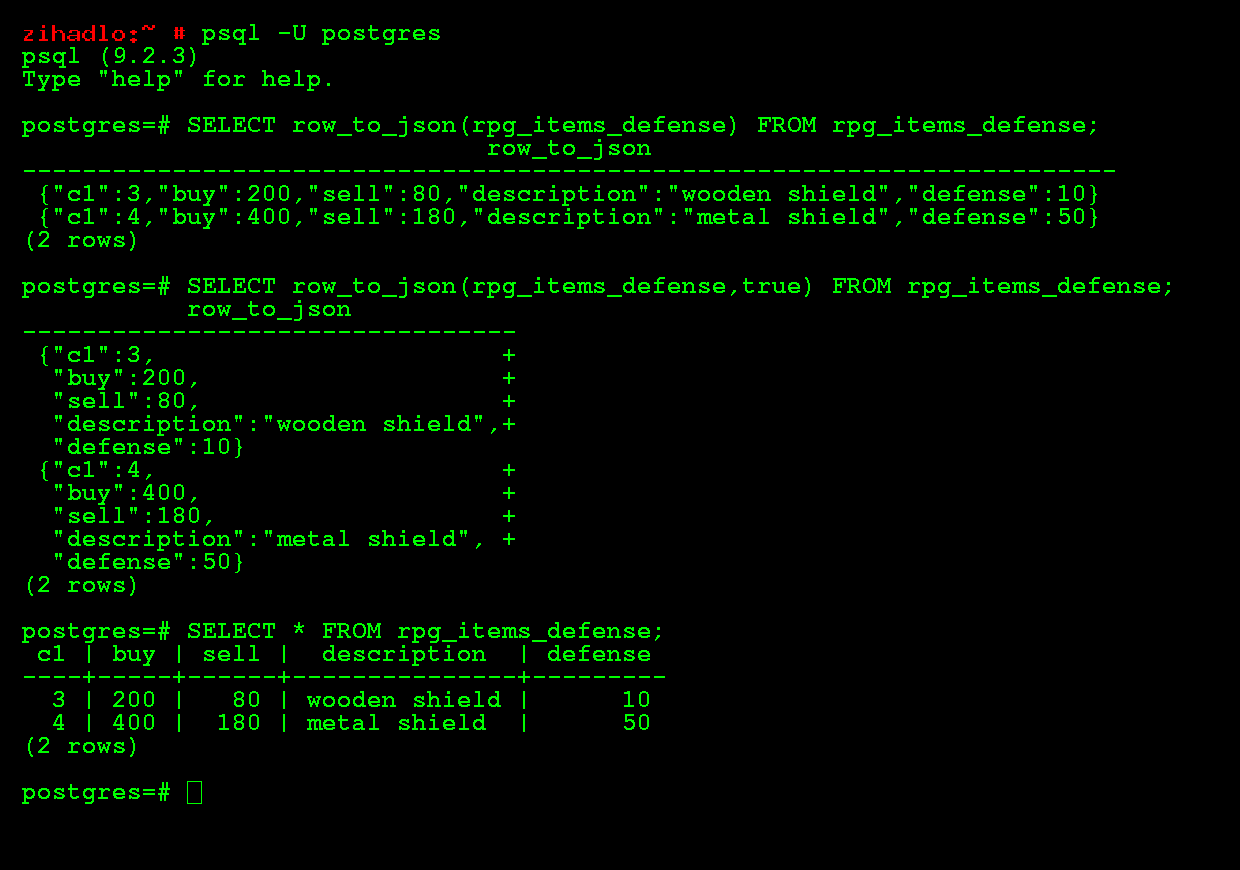
PostgreSQL 9.2 ships with openSUSE 12.3 and delivers native JSON support, covering indexes, replication and performance improvements, and many more new features. Native JSON support in PostgresSQL provides an efficient mechanism for creating and storing documents for web APIs. Range Types allow developers to create better calendaring, scientific, and financial applications. No other major SQL database supports this feature, which enables intelligent handling of blocks of time and numbers. See here for more information on this enterprise-class database.
openSUSE has moved from MySQL to MariaDB as default. MariaDB was first shipped with openSUSE 11.3 back in 2010. Over the years it proved itself and starting with 12.3 openSUSE is replacing default MySQL implementation with MariaDB. This means that whole distribution is compiled against MariaDB and in ‘M’ in LAMP means MariaDB from now. As MariaDB is a drop-in replacement, you don’t have to worry about compatibility. Apart from that, MySQL Community Server is not going away and you can still replace MariaDB with MySQL if you want.
If you've never heard about MariaDB, you can read more about all the cookies they have on their website. Especially more storage engines, speed optimizations and some other added features.
Infrastructure monitoring tool Nagios 3.4.4 adds bugfixes as well as a plain html page option to allow users to disable PHP and the loading of external references.
The latest Nmap supports 12 new protocols and the Squid web cache was updated to version 3.2.6, bringing the following main features:
- SMP scalability
- Surrogate/1.0 protocol extensions to HTTP
- Client Bandwidth Limits
- Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6)
- Squid-3.1 adds native support for streaming protocol ICY. Also commonly known as SHOUTcast multimedia streams.
- ICAP implementation (RFC 3507 and www.icap-forum.org)
Cloud
12.3 is the first release of openSUSE to feature complete packages for OpenStack, the leading open source cloud computing platform (12.2 had some packages from the Diablo release, but not the full set of packages required to run OpenStack). As OpenStack is made of many different components and servers, it is highly recommended to read the upstream documentation. On top of that, packages for Grizzly (next release of OpenStack due in April) are already being worked on and will be available for 12.3.
Highlights of the Folsom release (see the Folsom release notes):
- PKI support for authentication (in keystone)
- return of Hyper-V support (in nova)
- support for versioned objects in object storage (in swift)
- new API and client tool for image service (in glance)
- image replication (in glance)
- new service for network (quantum)
- new service for block storage (cinder) (used to be nova-volume)
- improved web dashboard
- several other features, tons of stability and performance improvements, as well as bug fixes
Finally, the DevStack tool which is used by developers to work on openSUSE has been ported to openSUSE. It makes it much easier to contribute to OpenStack from openSUSE, or to simply test OpenStack.
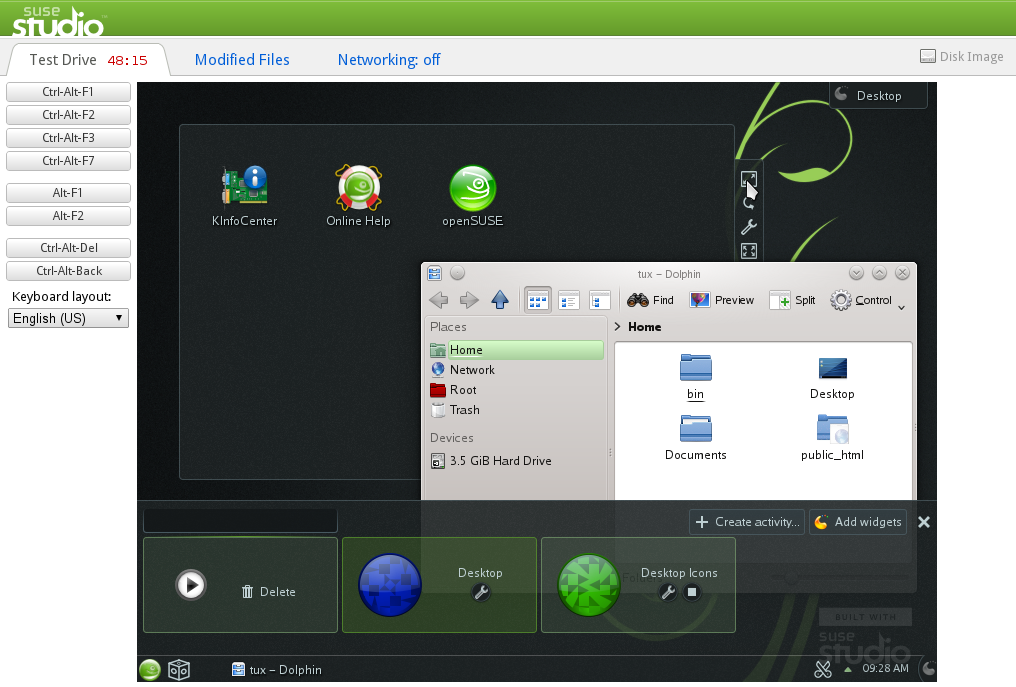
SUSE Studio is a project from openSUSE sponsor SUSE™ which builds upon the Free and Open Source openSUSE tools like KIWI and offers a convenient web interface for easy building of openSUSE and SLE based custom operating systems (appliances).
SUSE Studio users can expect availability of openSUSE 12.3 right from the release date, and support for upgrading existing appliances shortly after. This means it will be possible to easily create your own operating system for the cloud, desktop or portable devices based on openSUSE 12.3 with a custom package selections, artwork, scripts and any other properties. You can share your appliance or also browse other’s shared appliances on SUSE Gallery.
Live Images
Recovery Live Image
With the release of openSUSE 12.3 an additional, non-installable live image is provided for rescue and recovery purposes. It currently weighs in at 570MB and is thus considerably lighter than the GNOME/KDE live images and still fits on a CD-R. The new rescue live image is based on Xfce and thus provides an intuitive desktop environment with a number of applications allowing users to seek support, diagnose and recover from issues on their systems.
Apart from the core Xfce applications like the Thunar file manager, we have tried to ensure the rescue image keeps all the support channels to openSUSE accessible. So we have
- Midori, a lightweight browser which enables one to report bugs, access to search engines and forums, and allows one to send receive emails from a web based client
- ePDFreader, a PDF viewer for reading pdf manuals, and
- XChat, an IRC client enabling access to the the openSUSE community support channel at irc://freenode%23opensuse
For rescue and recovery purposes the rescue image contains
- gparted (and YaST's disk manager) for editing partitions on the hard disk,
- a small subset of relevant modules from YaST including bootloader manager, network device manager, remote administration (VNC),
- command line tools for data recovery like dd_rescue which is useful to rescue data in case of I/O errors because it does not necessarily abort or truncate the output and photorec, a data recovery utility,
- tools for data backup such as grsync, a graphical interface to rsync, and lftp, a feature rich command line ftp client.